When School Nurses Are Not Enough
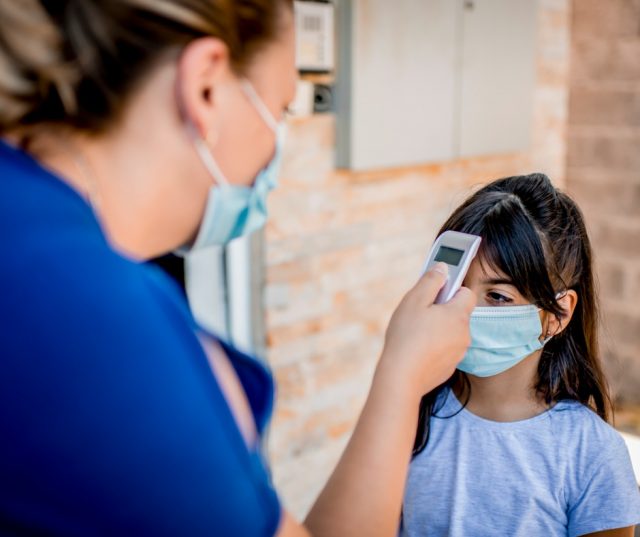
There is no better time than now to bump up the health resources for children in schools, experts say.
School children have had an especially challenging time navigating the tedious months of the pandemic, with recent reports showing that students fell four to seven months behind in math and reading compared to previous years, and with the most vulnerable students showing the steepest declines.
But while schools have typically tried to improve student achievement by focusing on academic testing and additional classes, they’ve too often neglected a major factor in their success: physical, mental and social health. This is especially true for children living in economically disadvantaged communities, who unlike their peers in wealthier communities often lack access to quality health care and resources.
There are many reasons such children often struggle to do well in school, but education specialists say there is no better time than now to devote more resources to their often-limited access to needed health services. Just as shouting doesn’t enable a deaf person to hear or better lighting a blind person to see, feeding facts and figures to youngsters with untreated health problems is unlikely to help them learn.
Charles E. Basch, a professor of health and education at Columbia University’s Teachers College, wrote in a special issue of the Journal of School Health in 2011: “Healthier students are better learners,” a fact he called “a missing link in school reforms to close the achievement gap.” In the report, he said that schools trying to enhance academic achievement should target their efforts on reducing health disparities that might impair a student’s education.
“The health needs of children have not been considered a central mission of schools,” Dr. Basch told me. “Yet there’s a clear connection between mental and physical health and the ability of children to learn.” And by not adequately addressing such needs, he said, “society is losing talent.”
Bringing health care to schools
Enter school-based health centers — facilities either in the school itself or nearby that not only tend to acute health issues like cuts and bruises, but also provide a suite of health services including primary, mental and dental care; substance abuse counseling; nutrition education and more. “They bring health care to where the children are, and they’re a very good way to provide health care to children who might not otherwise get it,” said Nicholas Freudenberg, a professor of public health at the City University of New York School of Public Health.
School-based health centers are a cardinal feature of community schools and other public schools that have increasingly recognized how difficult it is for many children to get their health problems adequately detected and treated. Such challenges may be especially acute for those living in low-income urban centers or rural areas. If a parent has to take time off from work or find a babysitter, or if transportation is unavailable or unaffordable to get a child to a medical visit, needed services are too often neglected until there’s a crisis, experts have said.
The nonprofit Paramount Health Data Project, which recently published a report on students’ health conditions in public and private schools in Indiana, found that the more often children visited the school nurse, the poorer their academic achievement on statewide tests, Azure Angelov, the project’s director, told me. The project’s data suggest “that students who are frequent visitors to the school nurse are simply unhealthy and frequently do not feel well during the school day,” Dr. Angelov and colleagues wrote in the report. “This is impacting their ability to learn.”
Although the majority of public schools have at least one full-time or part-time nurse, that’s hardly adequate to care for kids who often have complex and interrelated health problems that can get in the way of learning. For example, a child with poorly controlled asthma may avoid exercise and have trouble sleeping, which is when the brain consolidates memory. In addition to medication and routine follow-up, that child may need dietary and exercise advice and assistance in clearing allergens from the home.


Nurses Influence the Health and Wellbeing of Patients Every Day
As individuals, nurses directly influence the health and wellbeing of patients every day. Through frequent contact, nurses are best placed to encourage lifestyle changes in…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Changes in Nursing
Changes in nursing involve a major shift in higher education standards, requiring more nurses to hold a 4-year bachelor of science in nursing (BSN). The…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Trades make a comeback with Gen Z Workers
America’s skilled trades — from nursing and plumbing to welding to construction — need more workers as boomers retire. Gen Z-ers are stepping up to fill…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Congratulations, Sumner College Graduates: Embracing New Beginnings
Congratulations to the new Sumner College nursing graduates. As the tassels are flipped and mortarboards soar into the sky, a chapter closes, and another begins.…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
April BSN Info Sessions
Have you considered being a nurse and working in the healthcare industry? Attend an information meeting with Sumner College to learn more about the BSN…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
The State of Wellness: Everything You Need to Know About the Oregon State Board of Nursing
You have likely heard about the Oregon State Board of Nursing (OSBN), but how does the organization interact with and support Oregon nurses? Join us…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
OCN Explores Nursing Wages in New Research
Article & Photo Shared from Oregon Center for Nursing How much do Oregon nurses really make? The well-being of Oregon’s nursing workforce is a guiding initiative for…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
New Classes Start Today!
March classes start today! Welcome to our new BSN, PN and RN-BSN students.…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Meet Alex – Sumner College Graduate
Alex, congratulations on your graduation! As you’ve embarked on your nursing journey, remember: ‘Nursing is not just a profession, it’s a calling to serve, heal,…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Meet Alexandra – Sumner College RN to BSN Graduate
Alexandra, congratulations on your graduation! As you’ve embarked on your nursing journey, remember: ‘Nursing is not just a profession, it’s a calling to serve, heal,…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Meet Renee – Sumner College Graduate
Renee, congratulations on your graduation! As you’ve embarked on your nursing journey, remember: ‘Nursing is not just a profession, it’s a calling to serve, heal,…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Meet Serena – Sumner College Graduate
Serena congratulations on your graduation! As you’ve embarked on your nursing journey, remember: ‘Nursing is not just a profession, it’s a calling to serve, heal,…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Meet Amanda – Sumner College Graduate
Amanda, congratulations on your graduation! As you’ve embarked on your nursing journey, remember: ‘Nursing is not just a profession, it’s a calling to serve, heal,…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Meet Natalie – Sumner College Graduate
Natalie, congratulations on your graduation! As you’ve embarked on your nursing journey, remember: ‘Nursing is not just a profession, it’s a calling to serve, heal,…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Now Hiring
Are you a healthcare educator? Sumner College is looking for our next Nursing Educator to join our team. This is a part time position. Read…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Meet Erin – Sumner College Graduate
Erin, congratulations on your graduation! As you’ve embarked on your nursing journey, remember: ‘Nursing is not just a profession, it’s a calling to serve, heal,…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Exploring the Vital Role of Nurses in Heart Health
Article Shared from DiversityNursing.com February is American Heart Month. It's important to promote cardiovascular health and explore the many ways Nurses are engaged in these…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Meet Anne Marie – Sumner College Graduate
Anne Marie, congratulations on your graduation! As you've embarked on your nursing journey, remember: 'Nursing is not just a profession, it's a calling to serve,…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Nursing Ranked Most Trusted Profession for 22nd Year
Article Shared from DiversityNursing.com In Gallup's 2023 Honesty and Ethics poll, Americans' evaluations of almost all 23 professions have experienced a decline compared to previous years.…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Helpful Apps Every Nurse Should Have
Article shared from DiversityNursing.com Mobile apps have transformed how Nurses provide care to their patients. Smartphones allow Nurses easy access to applications designed to assist…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
DiversityNursing.com – Helpful Resources
Helpful Resources DiversityNursing.com is a Career Job Board, Community and Information Resource for all Nurses regardless of age, race, gender identity, religion, education, national origin,…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
How to Prepare for College – Oregon Goes to School
Article shared from Oregon Goes to College It’s a plan! No matter what grade you’re in, you can get ready for your future. Getting ready…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Sumner College Clinical Partners
Sumner College clinical partnerships play a crucial role in advancing medical education and training. By offering opportunities for hands-on experience and mentorship, these collaborations help…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Commencement Ceremony
Save the date - April 6, 2024 for Sumner College's Commencement Ceremony. Celebrating cohorts: PN54, PN55, ADN23, RN-BSN10 and RN-BSN11 Congratulations to you all!! Tickets…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Healthcare Hero
Are you aspiring to be a healthcare hero? A common question from our nursing students at Sumner College is about the role of ER nurses…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Dynamic – Interactive – Rich with Real-world Relevance
RNs are you ready to take your nursing career to the next level with a BSN? Guess what - at Sumner College, you can achieve…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
ER Nursing
Have you been thinking, “How can I start my nursing career in an ER?" Begin by obtaining a solid understanding of nursing through an approved…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
LPN
At Sumner College, we understand the importance of every role in the nursing field, including the dedicated work of Licensed Practical Nurses (LPNs). LPNs are…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Flexible – Balanced – Online RN to BSN
Wondering what it's like to pursue a nursing degree online? At Sumner College, our RN to BSN program fits the busy lives of working nurses…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn
Nursing, beyond direct patient care
Thinking about a career in nursing but interested in roles beyond direct patient care? At Sumner College, we recognize that nursing offers diverse career paths,…
Share at FacebookShare at TwitterShare at PinterestShare at LinkedIn